Systems manager: Systems Manager: 7 Powerful Roles That Transform IT Operations
If you’ve ever wondered who’s behind the seamless flow of technology in a modern organization, meet the systems manager — the unsung hero keeping digital engines running smoothly.
What Is a Systems Manager?

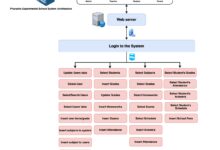
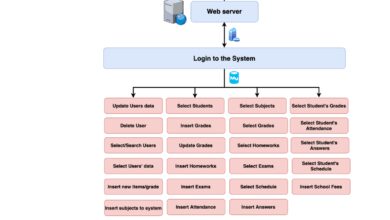
A systems manager is a pivotal IT professional responsible for overseeing, maintaining, and optimizing an organization’s computer systems and networks. This role sits at the intersection of technology, strategy, and operations, ensuring that hardware, software, and infrastructure function cohesively to support business goals. As technology evolves, so does the scope of a systems manager’s responsibilities — from managing on-premise servers to orchestrating cloud-based ecosystems.
Core Definition and Scope
The term systems manager can vary slightly depending on the industry, but at its core, it refers to someone who manages the lifecycle of IT systems. This includes planning, deployment, monitoring, troubleshooting, and upgrading systems. According to the U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics, professionals in this field are essential for maintaining organizational efficiency and cybersecurity.
systems manager – Systems manager menjadi aspek penting yang dibahas di sini.
- Manages both hardware and software infrastructure
- Ensures system reliability, scalability, and security
- Acts as a bridge between technical teams and business stakeholders
Evolution of the Role Over Time
Decades ago, a systems manager might have focused solely on mainframes and local networks. Today, the role has expanded dramatically due to cloud computing, remote work, and digital transformation. The modern systems manager must understand hybrid environments, DevOps practices, and automation tools. For example, platforms like Amazon Web Services (AWS) and Microsoft Azure have redefined what system management entails.
“The role of a systems manager has shifted from being a technician to becoming a strategic enabler of business innovation.” — TechLeaders Journal, 2023
Key Responsibilities of a Systems Manager
The day-to-day duties of a systems manager are diverse and demanding. They are tasked with ensuring that all technological systems operate efficiently, securely, and in alignment with organizational objectives. This section explores the primary functions that define the role.
System Maintenance and Upgrades
One of the most critical responsibilities of a systems manager is routine maintenance. This includes applying patches, updating software, replacing outdated hardware, and conducting system audits. Scheduled maintenance windows are often used to minimize downtime, especially in enterprise environments where uptime is crucial.
systems manager – Systems manager menjadi aspek penting yang dibahas di sini.
- Performs regular system health checks
- Implements firmware and OS updates
- Plans and executes hardware refresh cycles
Failure to maintain systems can lead to vulnerabilities. For instance, the 2017 WannaCry ransomware attack exploited unpatched Windows systems, affecting over 200,000 computers globally — a stark reminder of why proactive maintenance by a skilled systems manager is non-negotiable.
Network and Server Management
Systems managers are responsible for the configuration, monitoring, and optimization of servers and network infrastructure. This includes managing firewalls, load balancers, DNS settings, and virtual private networks (VPNs). In larger organizations, they may oversee a team of network administrators.
- Configures and monitors server performance
- Manages IP address allocation and routing
- Ensures redundancy and failover mechanisms are in place
Tools like Nagios, SolarWinds, and Zabbix are commonly used for real-time monitoring. A systems manager uses these platforms to detect anomalies, predict capacity issues, and respond to outages swiftly.
systems manager – Systems manager menjadi aspek penting yang dibahas di sini.
Security and Compliance Oversight
With cyber threats on the rise, systems managers play a vital role in safeguarding organizational data. They implement security policies, manage access controls, conduct vulnerability assessments, and ensure compliance with regulations such as GDPR, HIPAA, or PCI-DSS.
- Deploys antivirus, anti-malware, and intrusion detection systems
- Conducts regular security audits and penetration testing
- Manages user permissions and role-based access
According to a 2023 IBM Cost of a Data Breach Report, organizations with dedicated security management roles experienced 40% lower breach costs on average — highlighting the financial impact of effective systems management.
Essential Skills for a Successful Systems Manager
Becoming a competent systems manager requires a blend of technical expertise, problem-solving ability, and leadership skills. The role demands continuous learning due to the rapid pace of technological change.
systems manager – Systems manager menjadi aspek penting yang dibahas di sini.
Technical Proficiency
A systems manager must be fluent in multiple operating systems (Windows, Linux, Unix), networking protocols (TCP/IP, DNS, DHCP), and virtualization technologies (VMware, Hyper-V). Knowledge of scripting languages like PowerShell, Bash, or Python is increasingly important for automating repetitive tasks.
- Mastery of server administration and cloud platforms
- Familiarity with containerization (Docker, Kubernetes)
- Understanding of database management systems (MySQL, SQL Server)
For example, automating backup processes using PowerShell scripts not only saves time but reduces human error — a key advantage in high-stakes environments.
Problem-Solving and Analytical Thinking
When a system goes down, the systems manager is often the first responder. They must quickly diagnose the root cause, whether it’s a misconfigured firewall rule, a failing disk, or a DDoS attack. This requires logical thinking, attention to detail, and the ability to work under pressure.
systems manager – Systems manager menjadi aspek penting yang dibahas di sini.
- Uses diagnostic tools to isolate issues
- Applies structured troubleshooting methodologies
- Documents incidents for future reference and training
Effective problem-solving is not just about fixing issues but preventing them. A proactive systems manager will analyze logs and performance metrics to identify trends and preempt failures.
Leadership and Communication Skills
While technical skills are foundational, the ability to lead teams and communicate with non-technical stakeholders is equally important. Systems managers often present technical reports to executives, train junior staff, and collaborate with departments like HR, finance, and marketing.
- Translates technical jargon into business terms
- Leads cross-functional IT projects
- Provides mentorship and performance feedback
As noted by Harvard Business Review, “Technical leaders who can communicate effectively are 30% more likely to drive successful digital transformations.”
systems manager – Systems manager menjadi aspek penting yang dibahas di sini.
Systems Manager vs. Other IT Roles: Understanding the Differences
The IT landscape is crowded with specialized roles, and it’s easy to confuse a systems manager with similar positions like network administrators, IT directors, or DevOps engineers. Understanding these distinctions is crucial for career planning and organizational structure.
Systems Manager vs. Network Administrator
While both roles deal with infrastructure, a network administrator focuses primarily on the network layer — routers, switches, and connectivity. In contrast, a systems manager has a broader scope, encompassing servers, operating systems, applications, and integration with the network.
- Network admin: OSI Layer 2–3 (Data Link & Network)
- Systems manager: Layers 4–7 (Transport to Application)
- Systems manager often oversees network admins in larger organizations
For example, if email servers are slow, the network admin checks bandwidth and latency, while the systems manager investigates server load, disk I/O, or application bottlenecks.
systems manager – Systems manager menjadi aspek penting yang dibahas di sini.
Systems Manager vs. IT Director
The IT director is a strategic leadership role focused on budgeting, long-term planning, and aligning IT with business goals. A systems manager, while sometimes reporting to the IT director, operates at a tactical level — implementing and maintaining the systems that support those strategies.
- IT director: Sets vision and policy
- Systems manager: Executes and optimizes operations
- Systems manager provides technical insights to inform directorial decisions
In smaller companies, one person may wear both hats, but in enterprises, the distinction ensures clarity of responsibility.
Systems Manager vs. DevOps Engineer
DevOps engineers emphasize automation, continuous integration, and deployment (CI/CD) pipelines. While there’s overlap — especially in cloud environments — the systems manager typically has a wider operational remit, including legacy systems and end-user support.
systems manager – Systems manager menjadi aspek penting yang dibahas di sini.
- DevOps: Focus on code deployment and agile workflows
- Systems manager: Ensures stability and uptime of production environments
- Collaboration between the two is key for smooth operations
According to a Stack Overflow Developer Survey 2023, 68% of DevOps teams rely on systems managers for infrastructure stability during deployments.
Tools and Technologies Used by Systems Managers
No systems manager can operate effectively without the right toolkit. From monitoring software to automation platforms, the technologies used today empower managers to maintain complex environments with precision and efficiency.
Monitoring and Management Platforms
Real-time visibility into system performance is essential. Tools like Nagios, PRTG, and Datadog allow systems managers to track CPU usage, memory consumption, disk space, and network traffic across hundreds of devices.
systems manager – Systems manager menjadi aspek penting yang dibahas di sini.
- Set up alerts for abnormal behavior (e.g., 95% CPU usage)
- Generate performance reports for stakeholders
- Integrate with ticketing systems like Jira or ServiceNow
For instance, Datadog’s cloud monitoring capabilities enable systems managers to oversee hybrid environments — a necessity in today’s distributed IT landscape.
Automation and Scripting Tools
Automation is a game-changer. Systems managers use tools like Ansible, Puppet, and Chef to automate configuration management, reducing manual errors and deployment time.
- Automate user provisioning and deprovisioning
- Standardize server configurations across environments
- Deploy security policies at scale
A single Ansible playbook can configure 100 servers in minutes — a task that would take days manually. This efficiency is why automation is now a core competency for any systems manager.
systems manager – Systems manager menjadi aspek penting yang dibahas di sini.
Cloud and Virtualization Technologies
With over 90% of enterprises using cloud services, systems managers must be proficient in platforms like AWS, Azure, and Google Cloud. They manage virtual machines, storage buckets, and serverless functions, often using Infrastructure as Code (IaC) tools like Terraform.
- Deploy and manage VMs in the cloud
- Optimize cloud costs through resource tagging and auto-scaling
- Ensure compliance with cloud security best practices
According to Gartner, cloud spending will exceed $600 billion by 2024, making cloud fluency essential for every systems manager.
Career Path and Advancement Opportunities for Systems Managers
The career trajectory for a systems manager is both dynamic and rewarding. With experience and certifications, professionals can advance into senior technical or leadership roles.
systems manager – Systems manager menjadi aspek penting yang dibahas di sini.
Entry-Level to Mid-Career Progression
Most systems managers begin their careers as IT support specialists, system administrators, or network technicians. After gaining 3–5 years of hands-on experience, they move into systems management roles.
- Start with certifications like CompTIA A+, Network+, or CCNA
- Progress to roles like Senior Systems Administrator
- Gain experience with enterprise-grade systems and projects
Many employers value practical experience as much as formal education, especially in fast-paced tech environments.
Senior and Leadership Roles
With additional expertise, systems managers can advance to positions such as IT Manager, Director of Infrastructure, or Chief Technology Officer (CTO). These roles involve strategic planning, budget oversight, and leading large IT teams.
systems manager – Systems manager menjadi aspek penting yang dibahas di sini.
- Oversee entire IT departments
- Lead digital transformation initiatives
- Advise executive leadership on technology investments
According to PayScale, the average salary for a systems manager is $85,000, while IT directors earn over $120,000 — a clear incentive for career growth.
Specialization and Niche Expertise
Some systems managers choose to specialize in areas like cybersecurity, cloud architecture, or DevOps. Specialization can lead to roles such as Cloud Systems Manager, Security Operations Manager, or Automation Architect.
- Obtain advanced certifications (e.g., CISSP, AWS Certified Solutions Architect)
- Focus on emerging technologies like AI-driven operations (AIOps)
- Contribute to industry conferences and publications
Specialists often command higher salaries and greater demand in the job market.
systems manager – Systems manager menjadi aspek penting yang dibahas di sini.
Challenges Faced by Systems Managers Today
Despite the rewards, the role of a systems manager comes with significant challenges. From security threats to skill gaps, these professionals must navigate a complex and ever-changing landscape.
Cybersecurity Threats and Data Protection
With ransomware, phishing, and zero-day exploits on the rise, systems managers are on the front lines of defense. They must stay ahead of threats by implementing robust security measures and educating users.
- Deploy multi-factor authentication (MFA)
- Conduct regular employee training on security awareness
- Implement endpoint detection and response (EDR) solutions
The 2023 Verizon Data Breach Investigations Report found that 74% of breaches involved human error — underscoring the need for proactive security management.
systems manager – Systems manager menjadi aspek penting yang dibahas di sini.
Managing Remote and Hybrid Workforces
The shift to remote work has expanded the attack surface and increased the complexity of system management. Systems managers must ensure secure access to corporate resources from diverse locations and devices.
- Deploy zero-trust security models
- Manage mobile device management (MDM) solutions
- Support virtual desktop infrastructure (VDI)
Tools like Microsoft Intune and Cisco AnyConnect have become essential in this new era of work.
Keeping Up with Technological Change
Technology evolves at breakneck speed. Systems managers must continuously learn new tools, platforms, and best practices to remain effective.
systems manager – Systems manager menjadi aspek penting yang dibahas di sini.
- Attend industry conferences and webinars
- Participate in online courses (e.g., Coursera, Pluralsight)
- Join professional organizations like ISACA or CompTIA
Lifelong learning is no longer optional — it’s a job requirement.
Future Trends Shaping the Role of Systems Manager
The future of systems management is being reshaped by automation, artificial intelligence, and decentralized computing. Staying ahead of these trends is crucial for long-term success.
Rise of AI and Machine Learning in System Management
AI-powered tools are beginning to predict system failures, optimize performance, and even respond to incidents autonomously. This shift toward AIOps (Artificial Intelligence for IT Operations) is transforming how systems managers work.
systems manager – Systems manager menjadi aspek penting yang dibahas di sini.
- Use AI to analyze log data and detect anomalies
- Automate root cause analysis
- Reduce mean time to resolution (MTTR)
Companies like Google and Amazon already use AI to manage their massive infrastructures — a trend that will trickle down to smaller organizations.
Edge Computing and Decentralized Systems
As IoT devices proliferate, data processing is moving closer to the source — the edge. Systems managers will need to manage distributed systems across multiple locations, from factories to retail stores.
- Deploy edge servers and gateways
- Ensure low-latency communication
- Secure edge devices against physical and cyber threats
According to IDC, global spending on edge computing will reach $274 billion by 2026.
systems manager – Systems manager menjadi aspek penting yang dibahas di sini.
Increased Focus on Sustainability and Green IT
Organizations are under pressure to reduce their carbon footprint. Systems managers play a key role by optimizing energy use, consolidating servers, and migrating to energy-efficient cloud providers.
- Implement power management policies
- Use virtualization to reduce physical hardware
- Choose data centers powered by renewable energy
Sustainable IT is not just ethical — it’s increasingly a regulatory and competitive imperative.
What does a systems manager do?
systems manager – Systems manager menjadi aspek penting yang dibahas di sini.
A systems manager oversees the operation, maintenance, and security of an organization’s IT infrastructure, including servers, networks, and software systems. They ensure systems are reliable, scalable, and aligned with business needs.
What qualifications are needed to become a systems manager?
Most systems managers hold a bachelor’s degree in computer science or IT and have several years of experience. Certifications like CompTIA, CCNA, or AWS Certified SysOps Administrator can enhance career prospects.
systems manager – Systems manager menjadi aspek penting yang dibahas di sini.
Is systems management a good career?
Yes, systems management offers strong job growth, competitive salaries, and opportunities for advancement. With the increasing reliance on technology, skilled systems managers are in high demand across industries.
How is AI changing systems management?
systems manager – Systems manager menjadi aspek penting yang dibahas di sini.
AI is automating routine tasks, predicting system failures, and improving incident response. Systems managers are increasingly using AI-driven tools to enhance efficiency and reduce downtime.
What’s the difference between a systems manager and a network administrator?
A network administrator focuses on network infrastructure (routers, switches), while a systems manager has a broader role, managing servers, operating systems, applications, and integration with the network.
systems manager – Systems manager menjadi aspek penting yang dibahas di sini.
In today’s digital-first world, the systems manager is more than a technical operator — they are a strategic asset. From ensuring uptime to driving innovation, their role is central to organizational success. As technology continues to evolve, so too will the tools, challenges, and opportunities facing systems managers. By embracing continuous learning, leveraging automation, and focusing on security and sustainability, today’s systems managers can lead the way into a smarter, more resilient future.
systems manager – Systems manager menjadi aspek penting yang dibahas di sini.
Further Reading: